
-
May 27, 2022
Information on ITR filing, Process to file ITR, Income Tax Rate, and Income Tax Payment
For any taxpayer, it is important to know everything about income tax, ITR Returns, Slabs, and Tax Savings. This article will include all information on Income Tax Salary in India, Rate of Income Tax, how much income is taxable, and which income is exempt under the Income Tax Act. Income Tax is a type of Direct Tax levied on a person’s or a company’s earnings. The tax is calculated on the entity’s next taxable income based on income slabs established by the IT Department.
What is the Income Tax?
Individuals and businesses must pay income tax, which is a type of tax paid to the federal government on money earned within a fiscal year. One of the government’s primary sources of revenue is taxes. The government uses this money to, among other things such as create infrastructure, educate children, provide healthcare, and provide subsidies to farmers and the agricultural sector. Direct Taxes and Indirect Taxes are the two basic forms of taxes.
Different types of Income Tax Payers
-
Individuals
-
Companies
-
Firms
-
AOP (Association Of Persons)
Residents and Non-residents are likewise separated into two categories. Individuals living in India are required to pay taxes on their worldwide income, which includes money earned both in India and abroad. Non-residents, on the other hand, must pay taxes only on income earned or accrued in India. The residence status must be determined separately for each financial year depending on the length of stay in India for tax purposes.
Different types of Income Tax Forms in India
-
ITR 1
Individuals (residents) with a total income of up to INR 50 lakh and income from salary, one house property, other sources, agricultural income less than INR 5000.
-
ITR 2
Individuals/HUF (Hindu Undivided Family) who do not own or operate a business or profession.
-
ITR 3
HUF (Hindu Undivided Family)/Individuals who make a living via their own company or profession.
-
ITR 4
This return is for an Individual or Hindu Undivided Family (HUF) who is a Resident other than Not Ordinarily Resident, or a Firm (other than LLP) who is a Resident, with total income up to 50 lakh and income from a business or profession computed on a presumptive basis (u/s 44AD / 44ADA / 44AE) and income from house property, agriculture income up-to INR 5000, one house property, and other sources.
-
ITR 5
ITR 5 needs to be filled by LLP (Limited Liability Partnership) or for a Partnership Firms.
-
ITR 6
ITR 6 needs to be file by all the companies.
-
ITR 7
All the Trusts need to file Income Tax Return 7.
Required Documents for ITR (Income Tax Return) Filing
Some of the key facts/documents that you must have ready before completing your return are Form 26AS, Form 16, and Form 16A, proof of tax-saving investments made bank account details and others. Furthermore, the documentation you will need to prepare your tax return will be heavily determined by your source of income.
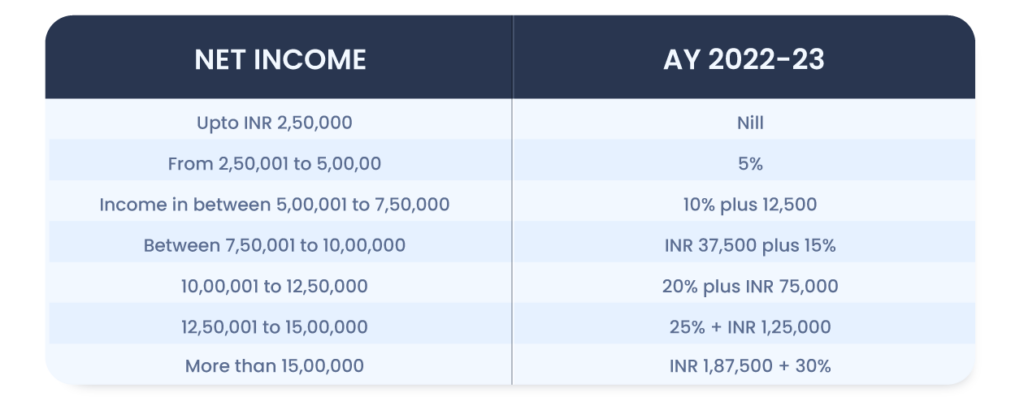
Information on Income Tax Rate for Individuals as per new Regime
The Process to File ITR (Income Tax Return)
A taxpayer can file ITR (Income Tax Return) in two ways :
-
Offline filing of ITR
-
Online filing of ITR
1. Process for Filing ITR Offline
-
Go to the Income Tax e filing portal.
-
Download the suitable ITR from IT Return Preparation Software.
-
Once the ITR is downloaded, extract the download utility file and open the Zip file.
-
Fill in all the necessary information and mandatory fields.
-
After that calculate the tax and validate the ITR form.
-
Save and Generate the XML.
-
Login to the portal.
-
Attach the XML file.
-
Once the file is attached, other requirements like DSC, Aadhar OTP verification will be followed.
-
The ITR will be submitted under the other two verification options, but the process of filing the ITRs will not be complete until it is verified.
-
The signed ITR should be delivered to CPC, Bengaluru, or the submitted ITR should be e-Verified later using the ‘My Account > e-Verify Return’ option.
-
The user needs to submit the ITR, and view the uploaded ITRs.
2. Process to file ITR Online
-
Login to the Income Tax E-filing Portal.
-
From the e-file menu click on the Income Tax Return link.
-
Select assessment year, ITR form number, and submission mode.
-
Once submission mode is selected online, Click on Continue.
-
Read the instructions carefully and complete all of the fields on the Online ITR Form that are appropriate and mandatory.
-
On the ‘Taxes Paid and Verification’ page, select the appropriate Verification option.
-
Select any of the e-verify options from the portal.
-
Once this process is done, click on Preview and Submit the ITR form.
-
Later, using the ‘My Account > e-Verify Return’ option or by providing a signed ITR-V to CPC, the filed ITR should be confirmed.
-
Now users can view the Uploaded ITRs.
Information on Income Tax Payment
-
Advance Tax
When a taxpayer’s expected income tax burden for the year exceeds Rs 10,000, he must pay the tax in advance. The government has set payment deadlines for advance tax installments.
-
TDS (Tax Deducted at Source)
When making payments to the recipient of income, the payer deducts tax at the source for certain amounts. By reconciling the TDS amount with the ultimate tax liability, the income receiver can claim the TDS amount as a credit.
-
E-Payment Facility
Taxpayers can pay advance tax and self-assessment tax online using the NSDL website. The taxpayer must, however, have a net banking account with an authorized bank.
-
Self-Assessment Tax
The balance tax is the tax that the taxpayer must pay on his or her assessed income. After subtracting the TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) and advance tax from the total income tax calculated on the assessed income, the self-assessment tax is calculated.
Information on Income Tax Saving
Tax preparation allows the taxpayer to save money on taxes. Investing in tax-saving instruments can help with tax planning. It aids in the reduction of income tax liabilities. Certain expenditures and investments can be deducted from total calculated income under sections 80C to 80U of the Income Tax Act.
A taxpayer can claim a tax advantage under Section 80D for health insurance premiums and medical expenses incurred for self, family, and parents additionally the 80C deduction. Section 80E allows a taxpayer to deduct interest paid on a loan taken for higher education. There is no limit to how much a deduction you can claim on your tax return.
A taxpayer can claim a deduction for interest paid on a housing loan during the relevant financial year under Section 24. Whether the house is self-occupied or rented out will determine the amount of the deduction. Section 80C allows the taxpayer to deduct the principal amount of the loan up to Rs 1.5 lakh. Section 80TTA of the Income Tax Act allows the taxpayer to claim a deduction for interest on bank deposits. Individuals can claim a deduction of up to Rs 10,000 under this clause.
FAQs on Income Tax
1. Is it possible to file a tax return even if my income is below the taxable threshold?
Yes, even if your income is less than the basic exemption amount, you can file a voluntary Income Tax Return.
2. What exactly is ITR-V?
After e-filing your Income Tax Return, you will receive an ITR-V, which is a one-page acknowledgment summary document. As a verification, you must print, sign, and mail it to the IRS within 120 days of e-filing your Tax Return. You can also use Aadhar or net banking to E-verify. None of the verifications are required if you filed using your DSC.
3. Is it necessary for me to e-verify in order to receive the IT refund?
To complete the ITR filing procedure, e-Verification of the electronically filed income tax return is required. Income Tax Returns should be e-verified within the deadline. ITRs that have not been confirmed will be considered invalid. You can use Aadhaar OTP, bank ATM, Electronic Verification Code (EVC), and net banking to e-verify your ITR.
Conclusion
The entire process of income tax collecting and return filing has been automated by the Income Tax Department of India in recent years. Individuals and Businesses have found it quite convenient to pay their Taxes Online, File Returns, and trace the history of their payments using the Income Tax Department’s different Portals.
ITR Filing
Filing of Income Tax return is necessary if you have earned any income. File your ITR with EbizFiling
About Ebizfiling -










Reviews
Ahmed Shaikh
23 Sep 2018Ms. Ishani and other team members are very helpful in the entire process of GST filing.
I really appreciate their support superb team.
Cheers!!!!*****
Chandrashekhar Nimmalwar
28 Oct 2020(Translated by Google) Ebizfiling has a company providing support for time period service and proper guidance. It is my personal experience at present. Chandrashekhar Nimmalwar. Today Aas Family Foundation (Original) ईबिज फायलीग की सेवा समय अवधि कार्य प्रणाली एव उचित मार्गदर्शन के लिए सहायता प्रदान कम्पनी है।यह मेरा वर्तमान में नीजी अनुभव है। चन्द्रशेखर निममलवार। आज आस परिवार फाउंडेशन
John Mello
13 Mar 2018I am associated with Ebizfiling since a year now. And all my IT returns and GST returns are managed successfully by them. Really happy with the services.
February 20, 2026 By Steffy A
Best Income Tax Software for Indian Taxpayers Introduction Filing Income Tax Returns (ITR) is a mandatory annual task for Indian taxpayers and often a stressful one. As per the Income Tax e-filing portal guidelines, taxpayers must submit their ITR […]
January 31, 2026 By Dhruvi D
Preparing and Filing Federal Tax Returns for US Taxpayers Introduction Filing federal tax returns is a yearly responsibility that many US taxpayers find stressful. The process often feels complicated because it involves multiple forms, deadlines, and rules that change […]
January 30, 2026 By Dhruvi D
Key Federal Tax Credits and Deductions for US Taxpayers Begin With, Many US taxpayers pay more tax than required simply because they are not aware of available federal tax credits and deductions. These benefits are designed to reduce tax burden, […]